Best Boron
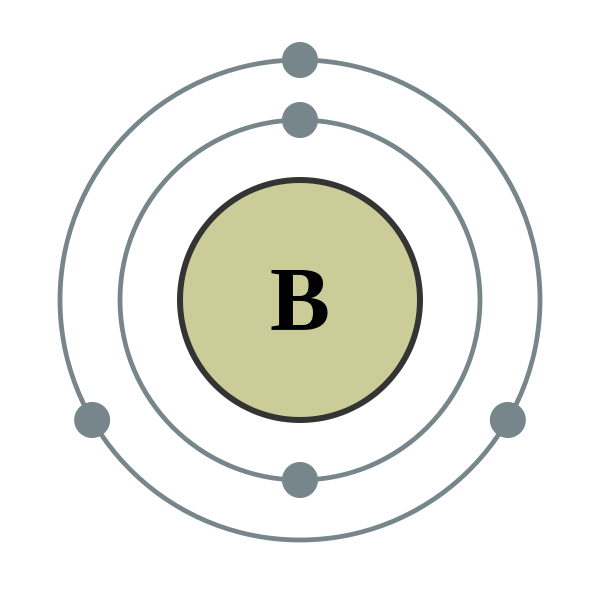
Boron is the fifth element on the Periodic Table.
Atomic Number: 5
Atomic Weight: 10.811
Melting Point: 2348 K (2075°C or 3767°F)
Boiling Point: 4273 K (4000°C or 7232°F)
Density: 2.37 grams per cubic centimeter
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Element Classification: Semi-metal
Period Number: 2 Group Number: 13 Group Name: none
Atomic Number: 5
Atomic Weight: 10.811
Melting Point: 2348 K (2075°C or 3767°F)
Boiling Point: 4273 K (4000°C or 7232°F)
Density: 2.37 grams per cubic centimeter
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Element Classification: Semi-metal
Period Number: 2 Group Number: 13 Group Name: none
History of Boron:
What's in a name? From the Arabic word Buraq and the Persian word Burah, which are both words for the material "borax."
Say what? Boron is pronounced as BO-ron.
Boron was discovered by three people, two working together and one working independently in the same year. (1808)
Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis-Jaques Thénard , were French chemists working together, while Sir Humphry Davy, an English chemist discovered the element on his own. Surprisingly, they all used the same method to obtain Boron, by combining boric acid with potassium.
Harmful effects:
Elemental boron is not known to be toxic.
Characteristics:
Boron is a metalloid, intermediate between metals
and non-metals. It exists in many different crystal
lattice structures , some more metallic than others.
Metallic boron is extremely hard and has a very high
melting point.
Boron does not generally make ionic bonds, it forms stable covalent bonds.
Boron can transmit portions of infrared light.
Boron is a poor room temperature conductor of electricity but its conductivity improves markedly at higher temperatures.
Uses:
amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares (distinctive green colour), and rockets (as an igniter)
boric, or boracic, acid, is used as a mild antiseptic
borax, Na2B4O7.10H2O, is a cleansing flux in welding
borax, Na2B4O7.10H2O is a water softener in washing powders
boron compounds are used in production of enamels for covering steel of refrigerators, washing machines, etc.
boron compounds are extensively used in the manufacture of enamels and borosilicate glasses
boron compounds show promise in treating arthritis
10B is used as a control for nuclear reactors, as a shield for nuclear radiation, and in instruments used for detecting neutrons
boron nitride is as hard as diamond. It behaves like an electrical insulator, but conducts heat like a metal. It also has lubricating properties similar to graphite
the hydrides are sometimes used as rocket fuels
boron filaments, a high-strength, lightweight material, are used for advanced aerospace structures, .
lightweight compounds used for aerospace structures
boron filaments used in fibre optics research
Boric Acid is also used in North America for the control of cockroaches, silverfish, ants, fleas, and other insects.
Cost:
Boron costs $5.00 per gram.
What's in a name? From the Arabic word Buraq and the Persian word Burah, which are both words for the material "borax."
Say what? Boron is pronounced as BO-ron.
Boron was discovered by three people, two working together and one working independently in the same year. (1808)
Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac and Louis-Jaques Thénard , were French chemists working together, while Sir Humphry Davy, an English chemist discovered the element on his own. Surprisingly, they all used the same method to obtain Boron, by combining boric acid with potassium.
Harmful effects:
Elemental boron is not known to be toxic.
Characteristics:
Boron is a metalloid, intermediate between metals
and non-metals. It exists in many different crystal
lattice structures , some more metallic than others.
Metallic boron is extremely hard and has a very high
melting point.
Boron does not generally make ionic bonds, it forms stable covalent bonds.
Boron can transmit portions of infrared light.
Boron is a poor room temperature conductor of electricity but its conductivity improves markedly at higher temperatures.
Uses:
amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares (distinctive green colour), and rockets (as an igniter)
boric, or boracic, acid, is used as a mild antiseptic
borax, Na2B4O7.10H2O, is a cleansing flux in welding
borax, Na2B4O7.10H2O is a water softener in washing powders
boron compounds are used in production of enamels for covering steel of refrigerators, washing machines, etc.
boron compounds are extensively used in the manufacture of enamels and borosilicate glasses
boron compounds show promise in treating arthritis
10B is used as a control for nuclear reactors, as a shield for nuclear radiation, and in instruments used for detecting neutrons
boron nitride is as hard as diamond. It behaves like an electrical insulator, but conducts heat like a metal. It also has lubricating properties similar to graphite
the hydrides are sometimes used as rocket fuels
boron filaments, a high-strength, lightweight material, are used for advanced aerospace structures, .
lightweight compounds used for aerospace structures
boron filaments used in fibre optics research
Boric Acid is also used in North America for the control of cockroaches, silverfish, ants, fleas, and other insects.
Cost:
Boron costs $5.00 per gram.